Oil and Fat Engineering

Oil and Fat Engineering



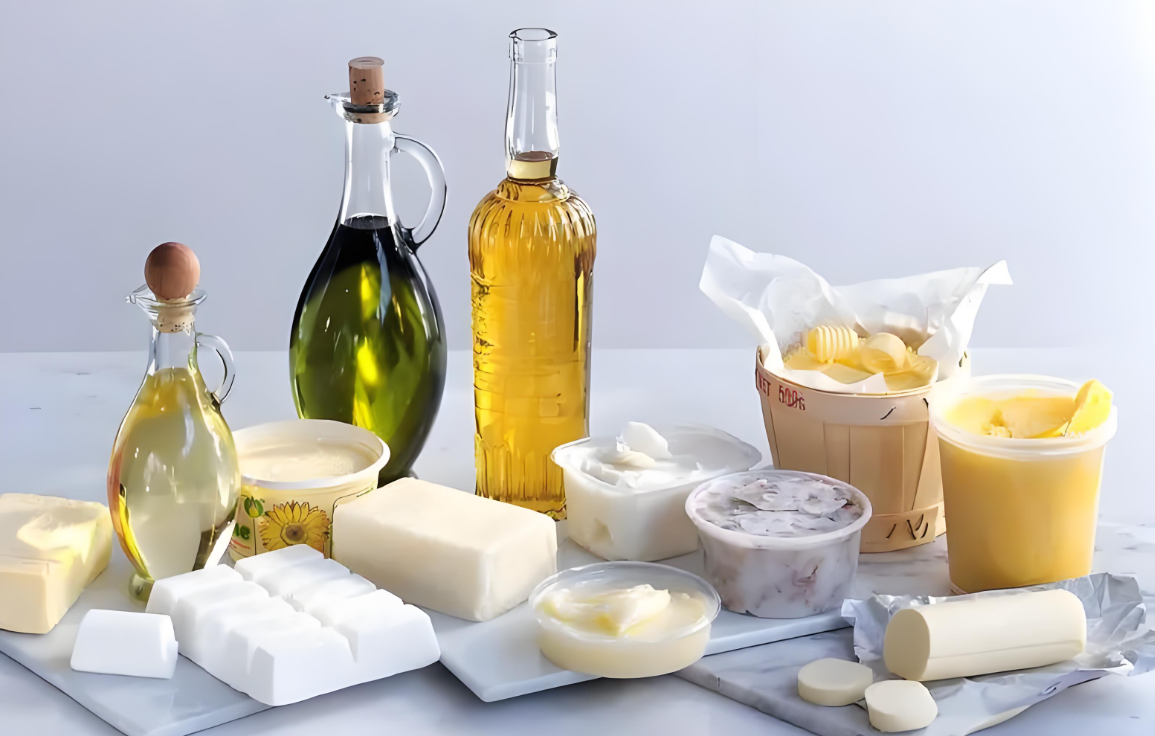
- Raw material selection: Choose suitable oil materials, such as vegetable oil (soybean oil, rapeseed oil, palm oil, etc.) or animal oil (lard, butter, etc.)
- Pre treatment: Clean, remove impurities, crush and other treatments on raw materials to remove impurities and improve oil extraction efficiency
Raw material selection and pretreatment
Oil refining
- Degumming: Removing the gelatinous substances from oil and fat, usually using water washing or acid washing methods
- Deacidification: Removing free fatty acids, usually through alkaline refining or physical deacidification methods
- Discoloration: Removing pigments from oils and fats, usually using adsorbents such as activated carbon or silica
- Deodorization: Removing odors and volatile components from oils and fats, usually through steam deodorization
Oil extraction
- Mechanical pressing: Extracting oil and fat through physical methods such as screw pressing, suitable for seeds with high oil content
- Solvent extraction: using organic solvents (such as hexane) to extract oils and fats, suitable for seeds with low oil content, with high extraction efficiency
- Supercritical fluid extraction: using supercritical carbon dioxide and other fluids for oil extraction has the advantages of environmental protection and high efficiency
Oil processing
- Hydrogenation: Treating fats and oils with hydrogen to alter their physical properties and improve stability, typically used in the production of margarine or solid fats
- Esterification: Reacting fatty acids with alcohols to form esters, commonly used in the production of biodiesel and food additives
- Fractionation: Separating oil and fat into different components to obtain high melting point and low melting point fats, suitable for specific purposes
 Online Service
Online Service

